—–0—–
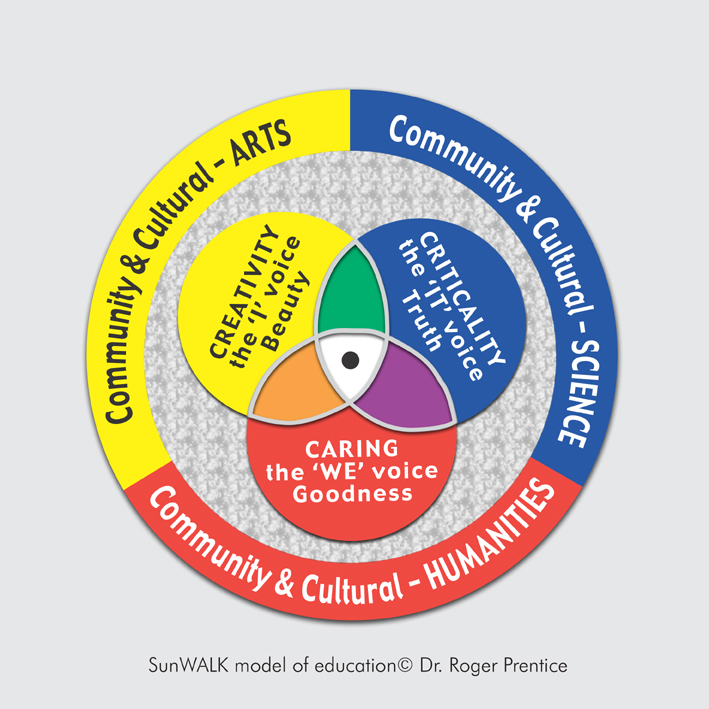
All postings to this site relate to the central model in the PhD. Summaries are HERE

The late, great Reg Bolton founder of ‘Circus-in-a-Suitcase’ which he took to many schools and youth groups and is the only person to have written a PhD about the vital importance of circus for young people.
Additional lecture-workshop 5: The New Circus and Holistic Education
Module description: This lecture-module looks at the New Circus, & Cirque du Soleil in particular to see what inspiration it might have for HE.
Key issues as questions: How and in what ways might the best of circus be inspiring in thinking about the development of (holistic) education?
How much might a physical skills lesson each day benefit children who find it difficult to concentrate on academic work? etc.
Essay text: Paper by RP SEE BELOW
Further readings:
Rings of Desire by Stoddart
Wings of Desire directed by Wim Wenders
Hard Times novel by Dickens (at least the first few chapters)
Hard Times video by BBC
Unpublished doctoral thesis by Dr Reg Bolton
Videos of Cirque dul Soleil – especially those that have on them documentaries about the behind the scenes work.
‘Deeper Levels of Yearning: Circus as encountering Mystical & Archetypal Experience’
“Every soul is a circus
Every mind is a tent
Every heart is a circus ring
Where the circling race is spent.”
Dedicated to:
The late Prof Ame Wilson
Dr Reg Bolton, founder of Circus in a Suitcase
Guy Lalibert, founder of Cirque du Soleil
Dr Roger Prentice
First presented at the Irfan Colloquium
Acuto, Italy
July 2005, revised February 2006
——————————–
ABSTRACT: In this paper I argue that circus is a deep
ritualistic form of art experience, through being
an external representation of the
dynamics of the interiority
of human consciousness. As such it can at best
be high art and provoke healing through
new realizations of wholeness.
Part I – Background and an Introduction to The Nature of Circus
What is circus?
In this paper I argue that circus is a deep ritualistic form of art experience that can resemble, or create, or metaphorically represent, the dynamics of the inner world of being human and as such can provoke healing through new realizations of wholeness.
Is circus an art form? – and one worthy of ‘serious consideration’?
Yes circus is an art form that creates culturally significant meaning, skilfully encoded in an affecting, sensuous medium (Richard Anderson). It communicates, via the senses, with little need for conscious intellectualizing. But it can be understood, and enjoyed at the consciously psycho-spiritual level as well. It is cross-cultural or trans-cultural or pre-cultural (archetypal-primordial) – even though it is traditional.
My own looking at circus as more than simply a diversion came first through reading ‘Rings of Desire’ by Dr Helen Stoddart, who lectures in film at the University of Keele and then through the work of Dr Ron Bolton in Australia, to whose as yet unpublished thesis I refer (see below).
What about the ‘New Circus’? Some 40+ million have bought tickets for Cirque du Soleil? Why are so many attracted, and why are a few antipathetic?
You can almost always find antipathetic views. In trying to make the anti case myself I could say that perhaps the 40+ million who have seen live performances are simply duped into a Disneyesque form of performance kitsch[i][i] But exactly what is sub-standard? The astonishing smooth organization, the sheer professionality, the Olympic level performers, the playing with the non-narrative and the narrative? Such negative critiques as I’ve come across seem to derive from a dislike of smooth professionality – as though grass-roots amateurism is the only legitimate form – and from prejudices or (inadequate) sensibilities concerning traditional circus. Why is aiming for the best in everything – costume, make-up, choreography, music, lighting etc – necessarily a contravention of traditional circus values? Being successful and big is also of course, in the UK mentality, sufficient reason for scorn. Another criticism seems to lie in the view that Cirque du Soleil is a hybrid of circus and theatre and multi-media art. So be it – this seems to be a strength and one which enhances, not diminishes traditional circus virtues of courage, humility, team-work and skilled performance.
Cirque du Soleil works for me, and it was the performance Quidam[ii][ii] in particular that converted me. The reason that this worked so powerfully for me is that it created an art performance that spoke deeply about human reality and its dreams via consummate performance skills. From it the aesthetic of traditional circus is retained but also moved on to a new level. Traditional circus is imagistic and ritualistic. It is a series of acts that follow each other as in the music-hall. Instead Quidam introduces a narrative element in which the acts are presented as events in an imaginary world of a girl who is living a boring life with her parents. For me the narrative transforms the cleverness and courage of the individual acts into the same level of high art as when the elements of opera really fuse. For some purists narrative might relegate new circus to mere ‘theatre’. In Quidam the girl, her family and the imaginary transformative world are kept at archetypal ‘everyman’ (person?) level, which is what makes it so powerful. Had the girl and her family been more important than the world to which they/we were introduced it would not have worked. The girl was every one of us.
Narrative is what creates access to philosophy in Matthew Lipman’s programme Philosophy for Children. PFC is the exemplary programme for developing the critical dimension in SunWALK, my model of holistic education. Narrative in Quidam, and in other Cirque du Soleil productions is, for me, transformative of a series of acts that would otherwise just be clever, courageous and admirable. The narrative creates the context, the deepest of contexts, in which to experience the texts of each brilliant act – and through this integration the performance as a whole become art of the highest form. Being human in the world with others is the eternal grand narrative that is not destroyed via postmodernism – it is not a privileged discourse, it is simply ‘the human discourse’. The presentation then for me has to be as it is in Quidam. That is at a level that is on the cusp between story and non-narrative archetypal quest – the ‘every-person’ level.
For Bolton circus, in its very nature, is composed of the same elements which characterize a fulfilled childhood. He argues that contemporary Western children can benefit from circus, especially the learning of circus skills, because it can make up for deficiencies in six vital experiences.
The six important experiences referred to are: self, risk, trust, dream, work and fun. These Dr Bolton sees as vital in a healthy childhood. He sees insufficient development and exploration of these as the cause of unhappiness (and of unsociable deviance). He sees development in circus skills as a remedial tool to enable youngsters, and indeed any of us, to re-connect with those essential dimensions of childhood. The idea being that this kind of learning can strengthen one or more of the areas in which an individual may have had insufficient development.
Within ‘self’ Dr Bolton includes ‘individuation’ which as a psychological term refers to [iii][iii]
“….. becoming an ‘in-dividual,’ and, insofar as ‘individuality’ embraces our innermost, last, and incomparable
uniqueness, it also implies becoming one’s own self.” —
CG Jung, Two Essays on Analytical Psychology, par. 266.
He (Bolton) 2004 p14 also calls upon Tennyson
The baby new to earth and sky
What time his tender palm is prest
Against the circle of the breast,
Has never thought that “this is I. “
But as he grows he gathers much,
And learns the use of “I” and “me”,
And finds “I am not what I see,
And other than the things I touch.”
So rounds he to a separate mind
From whence clear memory may begin,
As thro’ the frame that binds him in
His isolation grows defined. Alfred, Lord Tennyson, In Memoriam section 45. 1850
My concern as a teacher certainly includes nurturing individuation but here my concern is transcendence (see below) and transcendence can be thought of as de-individuation, the very opposite process to individuation. But this class of experience should not be thought of as homogenization; rather it is the experience of ‘no-self’. No-self is a temporary state, of fusion of the essential duality of ‘whole and parts’, through which we exist and develop. This dance of the opposites in life Ken Wilber describes like this:
“To understand the whole it is necessary to understand the parts. To understand the parts, it is necessary to understand the whole. Such is the circle of understanding.
We move from part to whole and back again, and in that dance of comprehension, in that amazing circle of understanding we come alive to meaning, to value, and to vision: the very circle of understanding guides our way, weaving together the pieces, healing the fractures, mending the torn and fractured fragments, lighting the way ahead – this extraordinary movement from part to whole and back again, with healing the hallmark of every step, and grace the tender reward.”
The Eye of Spirit; an integral vision for a world gone slightly mad
by Ken Wilber (1997) pub. Shambhala p.1.
The full state of at-one-ness is infrequent and temporary – fleeting even. For most people, once an individual has been brought into orientation with a great teacher, such as the Buddha or Christ or Bahá’u’lláh, then the process of (trying to) following the teachings is often seen as the attempt to achieve union more frequently and more deeply. An important issue that I later go on to examine is how far and in what ways are the religious and the aesthetic the same.
What kind of medium is circus? Theatre or ritual or what?
‘Circus is to theatre as poetry is to prose’. Anon (cited p in Bolton PhD)
The main difference people see between theatre and circus is that the former is dependent on narrative the latter on the imagistic in a series of acts, that can be traditional, which have no unifying narrative connections. Some purists might think that as soon as narrative comes in to a performance that calls itself circus that performance invalidates itself as circus – because it has become theatre. As I have argued above for me it is precisely the introduction of narrative, at least at the mythic level, that transforms the traditional form of circus into high art – along with high standards in all the media that are combined. This was a realization specifically through seeing Cirque du Soleil’s Quidam. For an educational model I wanted a form of the physical that was different to sport – this the New Circus provides. (As a bonus I also got a new extended metaphor for holistic education per se.)
It is clear that the New Circus and Cirque du Soleil specifically has made a tremendous impact on a variety of fields, as well as on individuals. Cirque du Soleil has been applauded by management and leadership organizations as well as the world of performance.
For individuals, there are the more than 40 million who have bought tickets, and the new form can be life-changing as in the story of Ohio University School of Theater professor Ame Wilson[iv][iv] who:
“had her masters’ thesis path set, until she saw a performance by Cirque du Soleil. “It was the most beautiful thing I’d ever seen,” Wilson told Polly Shulman of The New York Times. “I started to cry, and I sobbed the whole night. I knew that was what I had to study.” Soon after, Wilson, who heads the School’s Theater History, Criticism, and Dramaturgy program, began studying the famous outfit. After being denied access, she went “undercover” as a box-office employee, making friendships with those associated with Cirque. What emerged was her dissertation, “Cirque du Soleil Re-imagines the Circus: The Evolution of an Aesthetic,” which she’s expanding into a book.” Ohio University ‘Perspectives’ Autumn/Winter 2002
Later I discuss more how such how this form of art experience should go so deep, but the narrative combined with the imagistic and ritualistic seems to be at the heart of the new form of circus. Dr Bolton includes this interesting view – that ‘Circus is to theatre as poetry is to prose’. For me this connects with the view that circus (at least traditionally) is more about the imagistic than the narrative, but I prefer the creative possibilities of the multi-media to the purism of ‘no narrative’ separate acts. Thus perhaps we can call Cirque du Soleil’s Quidam ‘poetic-prose – in mythic form’. Perhaps the importance of this distinction between ‘poetry’ and ‘prose’ is related to the linear and the circular, the narrative and the ‘cinematic’, the masculine and the feminine, as well as to the word and the image.
In his thesis Dr Bolton points out that there is still a paucity of theoretical depth concerning the nature of circus. With characteristic humility and complete lack of foolhardiness I decided to present my own emergent reading of the humanistic and aesthetic nature of circus! Fools tread…….
Part II – Toward a ‘Maslowian Model and Aesthetic’ of the Circus
‘The heart has its reasons that reason knows nothing of.’
Blaise Pascal
I have chosen the Maslowian hierarchy as the basis for my reading of circus and its aesthetic. The version of the hierarchy I use is:
1) Physiological: hunger, thirst, bodily comforts, etc.;
2) Safety/security: out of danger;
3) Belonginess and Love: affiliate with others, be accepted; and
4) Esteem: to achieve, be competent, gain approval and recognition.
5) Cognitive: to know, to understand, and explore;
6) Aesthetic: symmetry, order, and beauty;
7) Self-actualization: to find self-fulfillment and realize one’s potential; and
8) Transcendence: to connect with something beyond the ego and help others find self-fulfillment and realize their potential.
http://chiron.valdosta.edu/whuitt/col/regsys/maslow.html
Elsewhere I have suggested that inverting the list also gives us a kind of cosmological model.
What attracts us to the (New) circus? In what do we delight? We go to the circus to be entertained and diverted, to admire, to laugh. But perhaps there is more. Circus can play with, and present opportunities to re-connect with, personal meaning at all of the eight Maslowian levels….. but here I am primarily concerned with the ‘deepest’, level – the transcendent.
The Malowian model is holistic. In what ways all of Maslow’s ‘levels of need’ provide a satisfactory framework for analysing the nature of circus generally. The levels are useful because they centre on what is always for me the ultimate question, ‘what it is to be (fully and positively) human?’ and as a student said, on a course on which I was teaching, ‘the origin of human rights is human needs’. We all need and have a right to be free from hunger, to be secure, to live in community, to have healthy self-esteem, have opportunities to continue to learn and to continue to be enriched by culture or the making of art, to take ourselves substantially toward our own perfection and finally to so relate to the Whole as to be relieved, on occasions, of the burden of self. Perhaps it is also true that we need to achieve this through service to others, rather than just through personal ‘consumption’. In leaving behind the other levels of need, and their associated rights, I turn to my main focus here on the level of transcendence.
Part III – Exploring ‘Transcendence’ in a Maslowian-Inspired Model of
Circus and its Aesthetic
The birds have vanished into the sky,
and now the last cloud drains away.
We sit together, the mountains and me,
until only the mountains remain.
Li Po
Being moved via identification
In circus, as in all arts with their potential to be deeply moving, we experience a close identification with the art object or performance. If we watch children particularly, their faces register the wonder and awe of the performance. Characteristically the individual is taken up by the performance and become one with it. This is particularly well known and manipulated it what is known as the ‘Hollywood movie’. But the experience is not confined to identification with a central character in circus. It is not only God who wondrous acts performs[v][v]. For the duration of the aesthetic experience we become at-one with the object or performance. Afterwards we are stunned. How stunned depends, of course, on the intensity of the experience. Later we can reflect and converse. What is made of the experience depends on the character of the individual and her or his circumstances. But potential for development lies in the ongoing effects of the experience.
Currently there is a surge of interest in the good that art does, or doesn’t do (SEE Carey 2005). For me there is not just the potential for good but also the potential for all of the other virtues, starting with truth, beauty and justice. Of course there is also the possibility of the negative – from the tacky to the downright corrupting. Art is neutral in the sense that it is the viewer that is sensible or not, morally alive or not, and the ‘charge’ from the art can, like science, be used for evil or good. It doesn’t generate goodness, but it provides energy for the person who would be good or more socially just. The story of German Nazis love of classical music whilst operating concentration camps is well known. Only if we are morally orientated in the first place can art be a nourishment for the positive and consequently the transcendence is for the good.
Through identification and being ‘taking up’, or ‘out of ourselves’, as is said in common parlance, we transcend our normal being. The state we experience temporarily is that of no-self, egolessness or no-boundaryness. As when entering water, or a wind-tunnel, we temporarily are relieved of the weight of self. Of course this is also what drugs provide. The answer to the need for drugs is true spiritual experience and enriched meaning-making. Enriched meaning made can provide the means for a more developed and positive self-image, especially when linked to serving others.
Individuals and groups need a conceptual and moral framework and impetus as well both transcendent experience and the criticality of reflection. Balance and happiness, in education and in society generally, lies in good combinations of all of these.
The circus as with any other art form presents us with the opportunity to be stirred through transcendence. As we have seen above the story of the late Dr Ame Wilson on first seeing a Cirque du Soleil performance illustrates this;
“It was the most beautiful thing I’d ever seen,” …… “I started to cry, and I sobbed
the whole night. I knew that was what I had to study.”
I doubt that many religious conversions exceed the depth of this persons ‘conversion’. But what was it that moves someone to such a depth, in such a way? In must be an apprehension of beauty and perhaps the vision of a superior way of being, and of living in a world more perfect. It must be a stirring of the very depths of the soul, at a level that is beyond normal narrative – a level that is archetypal and primordial. How do we see the aesthetic?
Weltzl (1991) reviewed four models used to analyze aesthetic experience and then proposed one of her own that combined elements from the earlier models. Her model, and one of the earlier models, included an initial identification or ‘fusion’ with the art object as the first stage in the aesthetic experience. Fairchild’s own model looks like this:
Fairchild’s model
Modes Phases Operational verbs
Dream Forgetting to fuse with
to orient oneself
to show feeling
to manifest emotion
Remembering to like, to dislike
to recall
to note
to associate
to state
to identify
Reflecting to separate from
to differentiate
to be aware of
Play Self-revelation to note significance
to re-order
to change signifier
to modify
to invent
Metaphor Describing to note, to describe
to associate meaning
to deconstruct
to note symbols
Structuring to order
to map
to structure
to categorize
to compare
Interpreting to explain
to discourse
to grasp meaning
to infer meaning
Concept Assessing to judge
to evaluate
to critique
to assess
In general I find the model satisfactory. My critique is that it is inadequate in placing ‘to fuse with’ as simply the first stage (operational verbs) of the sub-sub section (Phase ‘Forgetting’) of the sub-section ‘Dream’ of the model. Similarly the ‘like-dislike’ if it comes early is different to the ‘like-‘dislike’ that comes after a deep experience plus follow-up thinking, and probably researching. Real aesthetic experience ‘grabs you’ and forces suspension of the critical. This is true with either the ‘single image’ or the prolonged unfoldment in a film, opera or drama. I want to suggest something simpler and broader.
An aesthetic experience is, in my view, in two stages
a) undergoing it and
b) thinking about it, and otherwise ‘processing’ it, afterwards.
The key is simply this. In the first stage you are ‘taken’ by the piece with associative and critical faculties suspended. In the second stage the critical faculties and the articulation of associations and meaning come flooding in. This can be parallel to, or even a reverse of the process of creativity itself.
Possible further complications such as trying to re-create the experience, or meditating on the object or one of its parts, need not concern us at this point. A ‘high impact’ experience, the first stage, can seem timeless or out of time.
The second can be anything from a chat with a companion on the way home from a performance right through to a life-long re-orientation. In the latter case there seems to be no real distinction between aesthetic experience and what Maslow and other humanistic psychologists call peak experiences. Some might say that the first stage is the most important and that without some kind of ‘arresting’ or being ‘taken in’ there is no aesthetic experience to speak of.
Are ‘to orient oneself, to show feeling, to manifest emotion’ really appropriate under ‘forgetting’? If the fusion is an identification in which there is a loss of the sense of self then a sense of orientating oneself means that we have are turned to a state of duality – there has to be a self to re-orientate. The expression of emotion might come during the experience but, recollection, association, note-making etc I suggest come after the event, in which case they are part of the second of two stages.
I don’t want to spend time here on the ordering of the other various parts of the model but instead suggest a simpler model that in its second part can include the ‘modes, Phases and Operational Verbs’ as in Fairchild’s model. Prentice’s model then is happy to include all of the verb elements in Fairchild’s model but the really important right-brain and left-brain duality must be brought out in the most in the core bifurcation;
a) Identification (or ‘fusion’ or ‘transcendence’ or ‘at-one-ment’)
b) Processing the identification
These two stages are also characterised by loss of self or no-self, and on the other hand the return of self and a return of separateness and of a (new) relatedness.
Following the ‘identification’ we might immediately talk – to a companion or to our self internally. Alternatively we might be struck dumb and the experience might be so powerful that we can do nothing but weep for a whole night. The identification might lead to creative acts of our own – as opposed to cognition and talk. Play, metaphor and judgement are all important, but the arrangement of the analytical elements or even patterns of those elements in the talk or real people during and after aesthetic experience comes secondary to establishing the two stages of a) experience b) processing the experience.
We transcend through at-one-ment – which is why positive heroes and heroines are vitally important for the young. But what steps or approaches lead up to the possibility of such experience? Here I need to define terms, but without excluding alternative readings. Distinguishing between awe and wonder, two states attendant upon, at-one-ment, is particularly troublesome. If we enter the spiritual universe of one of the greatest writers on these ‘dimensions of the ineffable’, Abraham Joshua Heschel we might cease to be concerned by any need for distinctions, but distinction is needed in any more prosaic world.
Transcendence.
As a working definition I suggest that the ultimate stage is at-one-ment. Awe is next closest. It is from awe that we occasionally take the step off into the timeless in which we (temporarily) cease to be. Wonderment I suggest is next because although wonderment seems to include the sense of awe it in fact bifurcates into wonder as in ‘I wonder’. With ‘I wonder’ there is still the sense of self, or a return to the sense of self – and therefore of duality. I take transcendent experience and mystical experience to be the same – experience of at-one-ment. The mystical[1][1] I take to be no more, and no less, than Hick’s view (1981 p423) that:
” Mystical experience…..does not seem to me to be anything other than first-hand
religious experience as such. This is, however, the core of religion.
Heschel also uses the term ‘radical amazement’ as synonymous with wonder. In trying to define my terms, and accepting that others will see define awe, wonder, the ineffable etc differently I simple want to help describe what these terms may reveal in relation to our two basic ways of knowing. Heart knowing that flows from the transcendent experience via the ineffable and, secondly, head knowing via reason and academic application.
Our normal state is one of duality, of feeling with varying degrees of intensity the separate self. In addition to the full range of positive and negative emotions there is longing. The ultimate longing is for at-one-ment. Debased avenues to at-one-ment include drugs. Natural forms include sexual union. The spiritual is a matter of arriving at a unitive state of being – within some true form of moral and spiritual context. From this we can conclude that true religious experience, because of its contextualization in a religious belief system is unitive in the way described by Hick above but aesthetic experience, also unitive and transcendent is not necessarily religious – unless the person also undergoes the experience from with a religious belief system.
The transcendent experience, including ‘peak’ experiences, lasts for brief periods of time – seconds to hours (very rarely I suspect). The experience seems afterwards to be ‘out of time’. Before and after such unitive experiences there comes re-separation, the re-assumption of the duality of the ‘mantle of self’.
There is another way in which aesthetic and mystical experiences are the same. For me art is always more or less successful attempts at the impossible. Both are the products of the ineffable, of the impossible to render perfectly that which was envisaged. The impossibility of communicating the insights we glean from encounters with the ineffable, from the Whole. From a religious perspective God is one, and sometimes His presence is expressed in matter, sometimes in spirit or energy – all ways there is a trace that we sense but can never describe. Art is always the ‘failure’ of the mystic, the failure of ‘this is what I saw’, ‘this is what I experienced’, ‘this is the viewpoint of my subjectivity’. For me the Creation is an emanation of continuous creativity.
Here we are trying to articulate how the transcendent might be expressed – inevitably inadequately – at the highest levels of human experience, but perhaps we could also, to be holistic, describe an overall model to include experiences at all of Maslow’s levels of need. If we are ‘believers’ with a unitive world-view then there is another implication. Unless we set lower levels as being in opposition to the spiritual then slaking the thirst, or sexual union or friendship are also God working through His Creation. God works through subjectivity as well as objectivity (or more through subjectivity), He works through separation as well as being at-one. If all lower levels are contained within the context of the higher level then their import is not only unified but, through contextualization, holy.
In ‘separation’ we are in, or we re-enter the world of words. With images – at least those that are worthy of giving ourselves to – we are reminded of, or led to, at-one-ment. Perhaps we have with the New Circus a challenge to, and a solution for, getting the domains of word and image into a better balance?
Regret for the lack of balance between the head and the heart at the individual level has also been expressed:
“If I had my life to live over again, I would have made it a rule to read some poetry and listen to some music at least every week… The loss of these tastes is a loss of happiness, and may possibly be injurious to the intellect, and more probably to the moral character, by enfeebling the emotional part of our nature.” Charles Darwin (quoted in Christian p. 611)
Perhaps in the (new) circus we have the means to see better balances between head and heart, as well as between the imagistic and the narrative.
Part IV – The Word and Image – a New Balancing?
‘Circus is to theatre as poetry is to prose’. Anon (cited in Bolton PhD)
“I grew up surrounded by images and imagery. And
I put them into motion” – Daniele Finzi Pasca Creator and
Director for Corteo ( Cirque du Soleil production) – Quoted in Fascination
Newsletter No 43 April 2005 http://www.cirquefascination.com/
As we can see from Bahá’u’lláh’s ‘proofs’ the written word is a back-up for the Word of God for those that do not have the eyes to see, they are not in themselves the Word of God. In a sense they are a re-presentation of the Word of God. My understanding is that the Manifestation was the necessary intermediary between God and His Creation throughout all time. Given the eternity of Creation, and of God the Creator, then the fact that writing was a very recent invention constitutes a logical underlining of the distinction that Bahá’u’lláh makes.
Dancing and song came much earlier than writing – and so it seems did images. In the severely criticised yet useful current (May/June 2005) BBC TV series How Art Made the World we see that, so far as current evidence shows, image-making started long before writing – and writing of course is an adaptation, and ‘abstractification’ of sequences of images. The ‘wordification’ of humanity dates at least from Sumerian times. The oldest images seem to be 30-35,000 years old.
The experience of finding the paintings in the Ardèche caves, on 18 December 1994, by Jean-Marie Chauvet, Eliette Brunel Deschamps and Christian Hillaire is described like this:
‘Alone in that vastness, lit by the feeble beam of our lamps, we were seized by a strange feeling. Everything was so beautiful, so fresh, almost too much so. Time was abolished, as if the tens of thousands of years that separated us from the producers of those paintings no longer existed. It seemed as if they had just created these masterpieces. Suddenly we felt like intruders. Deeply impressed, we were weighed down by that feeling that we were not alone; the artists’ souls and spirits surrounded us. We thought we could feel their presence; we were disturbing them.’ http://beautymatters.blogspot.com/2000_01_05_beautymatters_archive.html
The story of art and myth is the story of one kind of knowing. Karen Armstrong in her latest book A Short History of Myth returns to the theme of ‘mythos and logos’ which features in several of her earlier books. In her review, of Creationism by Michael Ruse, written for the New Scientist (2005) Karen Armstrong provides a summary of her view of mythos and logos;
In the pre-modern world, it was generally understood that there were two ways of arriving at truth. Plato called them mythos and logos. Neither was superior to the other. Logos (reason; science) was exact, practical and essential to human life. To be effective, it had to correspond to external reality. Myth expressed the more elusive, puzzling aspects of human experience. It has often been called a primitive form of psychology, which helped people negotiate their inner world…
Myth could not help you create efficient technology or run your society. But logos had its limits too. If you became a refugee or witnessed a terrible natural catastrophe, you did not simply want a logical explanation; you also wanted myth to show you how to manage your grief. With the advent of our scientific modernity, however, logos achieved such spectacular results that myth was discredited, and now, in popular parlance a myth is something that did not happen, that is untrue. But some religious people also began to read religious myths as though they were logos.
The conflict between science and faith has thus been based on a misunderstanding of the nature of scriptural discourse. Many people, including those who are religious, find it difficult to think mythically, because our education and society is fuelled entirely by logos. This has made religion impossible for many people in the west, and it could be argued that much of the stridency of Christian fundamentalism is based on a buried fear of creeping unbelief.
In the pre-modern world, it was considered dangerous to mix mythos and logos, because each had a different sphere of competence. Much of the heat could be taken out of the evolution versus creation struggle if it were admitted that to read the first chapter of Genesis as though it were an exact account of the origins of life is not only bad science; it is also bad religion.
The duality of mythos and logos relates to many other dualities; heart and head, right-brain and left-brain, art and science, subjectivity and objectivity – and so on. In our world we have achieved a ‘complex of imbalances’, and hence a complex of dis-eases. Healing lies in an ‘antidote’ of re-balancings. (Without the surgical removal of creative tensions!)
In our world the word and the image are out of balance (words and images?)? Many kinds of imbalance could be considered; the power and consequences of the 20th century’s one new art form cinema: the fact that with each new medium the media that are supposed to be destroyed aren’t, the fact that with new media the sale of books goes up not down; the wailing about falling standards of literacy (the massive rise in the abilities of what I call ‘visuacy’ are never mentioned in the same breath); the rejection of representation by some forms of religion – and so on. The word and the image have had a tense relationship. Perhaps now in these post-modernist New Circus times we have the possibility of enjoying them in new forms of more positive and creative relationship, more equitably balanced forms.
Interestingly the words now sung in Circle du Soleil performances are not ‘real’. Productions might sound Spanish, French, or Italian, or even Chinese but the vocalists are singing variations of ‘gibberish’ which they call “cirquish.” This seems to me the greatest attempt at the ‘suppression’ or at least limiting of ‘meaning-interferences’ that I have heard of since I heard, many years ago, that the playwright Becket chose to write in French[2][2] in order to write with discipline and economy – and perhaps to remove his thought from the domination of its mother-tongue associations and connotations. For Becket it must have been a desire to gain lucidity by blocking out down childhood associations. I wonder if some people avoid going to the circus for similar reasons?
With its greater emphasis on dance and movement and (moving) images Cirque du Soleil offers a decoding of mega-rich (too rich?) communication that is not language-dependent. Not only is it more universal in the sense that you do not have to speak a particular language (with all of the historical and colonialist connotations it might evoke) it is more fundamentally universal in that it communicates at a pre-language, primordial level. And for someone who interested in the oneness of human kind it enables the particularity of culture to be woven into an expression about the universality of being human. Dance and mime are primordial and figure strongly in the language fabric of the (new) circus.
Two other interesting connections about non-verbal or pre-verbal communication are worth mentioning. Firstly there is the rise in interest in teaching babies a form of signing to enable better communication and reduce frustration. Secondly we find that for some hearing children of deaf parents BSL is their first language. Perhaps we too by turning to the circus can free ourselves from the domination of the left-brain focus on language. What benefits might there be if children had equal time and encouragement to use dance and mime, as well as speaking, reading and writing?
Perhaps the most radical statement about the stresses of the unhappy side of the relationship between word and image is to be found in Leonard Shlain’s contentious book The Alphabet and the Goddess (1998). Shlain (a Californian surgeon, suggests that:
“Literacy has promoted the subjugation of women by men throughout all but the very recent history of the West,” ….. “Misogyny and patriarchy rise and fall with the fortunes of the alphabetic written word.”
This is the dark side of what is usually thought of as a great step forward. The very act of learning written language, he argues, exercises the human brain’s left hemisphere–the half that handles linear, abstract thought–and enforces its dominance over the right hemisphere, which thinks holistically and visually. I have always preferred to think that it is better to think of masculine and feminine principles, that is with both as being part of men and women – although clearly gender consequences are clear and profound where society is organized in favour of one gender.
A sub-theme of the book is that over reliance on the left hemisphere “initially leads a society through a period of demonstrable madness.” We would all see contemporary madness in different ways. Perhaps there would be common elements – war and poverty would be on most people’s list. At very least it is interesting to speculate the consequences of a society that has a better balance between literacy and what I have called ‘visuacy’ – literacy’s imagistic equivalent. But as I suggested above there is also the need to use the body as an instrument of expression.
Traditional circus is strongly visual and non-narrative and does not require literacy – but it does require basic levels of visuacy. New circus has re-introduced narrative, I’m thinking particularly of Quidam, but it is still overwhelmingly visual and imagistic. Of course the visuals are mainly ones that move. Consequently the (new) circus is closer to art cinema than to theatre in that it is a sequence of images that offer meaning-making possibilities without enforcing too manipulatively a narrative and the feelings that are supposed to be felt (as in Hollywood narrative cinema where violin music tells you that you should be feeling sad at a particular point). Having recently seen Allegria in London, as well as several shows on DVD, the impression is that in Cirque du Soleil meaning is deliberately held at the artistic-mystic level at which we feed from the well according to our needs. Nor is circus simply bourgeois nicety – clowns and trapeze artists can be fear-inducing as well as laughter-inducing.
We should seek by every possible means to re-balance the ‘left’ and ‘right’, the literary and visual sides of our world not just to maximize creativity but also to achieve particular vital social concerns such as creating justice for women. But there is a reason that is even more fundamental as to why we should re-balance the left and right, the literary and visual sides of our world. That reason is simply that we are most fully whole, and therefore most fully human with such a balance. We are hard-wired to this reality and serious neglect on either side might seems to lead to catastrophic dysfunction.
Part V – Circus, the Inner Child and Yearning
‘Genius is nothing more or less than childhood recovered by
will, a childhood now equipped for self-expression with an adult’s capacities.’ Baudelaire
‘Play is the mother’s milk of the intellect.’
The adult’s sense of being adult includes ‘putting away childish things’. This means for many adult’s there is no ‘permission to play’. For the adult visiting the circus might only be legitimized through taking a child or grandchild. This permission via the vicarious enables the adult to re-connect – to associations that might have painful origins, or at least dark ones, as well as pleasurable. Cinema also offers adults some kind of replacement for the kind of awe and wonder that circus can afford the child and the ‘child in the adult’ – but as I’ve suggested it can be a much more manipulative medium.
Many adult lives are so stressed that truth-seeking and self understanding are a burden too far. If we habitually avoid the quest for self-understanding, and the possibility of consequent transformation, then perhaps visits to the circus (or pantomime or Punch and Judy or theatre) can stir deep levels of our consciousness. My own early memories centre on the sense of expectation, ‘what will happen?’…… The sense of place was also very important – the temporary tent, the smell of sawdust and animals, seeing others around the magic ‘O’, seeing more exotic others in the matrix of the ‘O’ – and being expelled therefrom.
To re-connect is a revisiting to a lost world – the world of the magic, and to some of the fright, of childhood experience in which things appear and disappear without causal explanation, or the need for causal explanation. The lost world has been called enchanted and it seems to me that the modern adult world is a world of disenchantment (Wilber: 19..), (Heschel: 19..). The negative side of the unbroken world of identification is a world of enchantment. It is a world of is isness and nowness. In it delight comes upon us or re-comes upon us. The world again becomes the joyous ‘all’ of the toy-shop window, the enormous cake, and the un-looked for present. Visiting the circus then is, potentially, an encounter with our deeper self (or selves). It can also be seen as a re-engaging with a quest, perhaps a quest that we, or life, denied. We are stirred and to be stirred is to be called to do something.
2 Circus as dialogic encounters with the child, who was ‘parent of the adult’
“It’s never too late to have a happy childhood.”
Relevant to the Bolton grass-roots participatory view of circus is Wordsworth’s ‘The Child is father of the man’. Presumably the girl is also mother of woman. The shaping effect of childhood experiences become the structures of adult personality. Of course with courage and the privilege of sufficient time and money we can engage in the quest for self-transformation, some of which comes un-asked for simply through life-events. Marriage and parenting of course bring opportunities to re-inforce our problems – or to transform ourselves into more free and angelic beings. The most awful thing I ever heard about parenting is the view that our children are a manifestation of our unconscious selves! In marriage lies not only the new but the possibility to transform the past.
As someone said there are, psycho-spiritually, at least six persons in every marriage. These are the two partners and their four parents. These four are real people who visit or require visits, or are as internalized dimensions in the two partners. We bring to marriage-relationships unresolved aspects of our relationships with parents as well as those that are resolved. The arts are one avenue for transformation, and integration, of the un-resolved. The arts are the means to raise consciousness, to respond to issues that have been resolved into complacency, or locked away as to difficult. (Heschel makes a similar argument for encounters with the ineffable within religion.) Quidam is an experience of a mythical world in which we can release, or vicariously have released, some of the very forceful daemons of childhood experience (SEE Rollo May’s Love and Will )
Transformation of hurts and stunted aspects of our development can be of major importance – with transformation we can grow in usefulness to others and therefore in personal happiness. Without such transformation we remain less than fully functioning, we remain in varying degrees of dysfunctionality. It’s never too late to have a happy childhood, as the saying goes. This was, and is, one of the most explosively insightful, and challenging, dicta I have ever heard because it carries the possibility and hope of release – through transformation.
In addition to Wordsworth Bolton quotes (p. ) Vachel Lindsay:
Every soul is a circus
Every mind is a tent
Every heart is a circus ring
Where the circling race is spent.
For me this fragment from a poem carries the bedrock idea for what I have been discussing – that the circus is an external representation of the dynamics of the interiority of human consciousness. If every soul is a circus in what sense is it so? The answer is that there is within the interiority of each of us the tussles of right and wrong, the dreams of soaring, the joy in colour and form and movement – many of Maslow’s levels of need, including those that relate to our highest selves. The ‘O’ of the circus ring is a representation of the human interiority. The fact that the race that is run, (by horses for example, in traditional circus) is circular is interesting in relation to the spiritual idea that we are confronted with challenges repeatedly until we master the required lesson. The ‘O’ as a ‘sacred’ space is much older than circus as we know it – it was the shape of early theatre and much earlier ‘parliaments’ and sacred spaces. It is the shape of many dwellings, and the shape of some temples. It is the symbol of the eternal. It is an arena in which acts are performed that are archetypal – and out of time. Far from being merely ‘entertainment froth’ the circus can consequently move us at levels deeper than the culture to which we belong. Circus at best is a revisiting of the at-one-ness experience of awe and wonder, of the world of enchantment, our own Garden of Eden, complete with a slither or two in the undergrowth. It is engagement with the earliest of humanity’s stirrings as well as our own early memories.
Of course for most of us, most of the time, deep in the cave the shadows of these tensions continue to flicker. When they are arranged into a complex, around negative childhood experience, they can be severely damaging to our functionality. But hope and the transforming power of love and the releasing power of art are also part of adult life.
Let us pose an even deeper, perhaps even more challenging, possibility that the circus at the deepest levels of stirring is not only archetypal but what we might call ‘pre-birthian’.
3 Childhood and Longing as re-visiting a more fundamental at-one-ment
‘
The heart has its reasons that reason knows nothing of.’
Blaise Pascal
Can we be stirred by the deepest of circus experience at a level even deeper than the re-activation of childhood memories through seeing and sensing again archetypal figures – SEE http://www.religiousworlds.com/fondarosa/jung03.html In Quidam the acts are embodiments of forces that play in the unconscious arena – and which break through in dreams or visions. As such they are stirrings that can be deeper than specific culture – and are they perhaps older than childhood?
Visiting the circus as re-connecting with intra-uterine experience
More fundamental, if not primordial, than re-connecting with childhood reality is a re-connecting with the reality of intra-uterine experience. In addition to the reality of childhood we are stirred more deeply down to that at-oneness with the mother in the womb and its explosive disturbance in parturition (the first of all journeys and perhaps the symbolic origin of all quests).
Birth is a violent separation from a ‘perfect’ state of being, from our own Garden of Eden. Birth is the origin of resentment, anger, sense of loss etc. – as well as of all positive emotions. As days, weeks and months go by we are no longer free of consciousness of self – we have shockingly begun the journey of discovering aloneness as well as the journey of individuation. We have ‘bitten’ into the apple. Some see the first stage of the realization of separateness as gradual – in say the early weeks or months. That is to say the child only gradually comes to understand that s/he is a separate entity from the mother (cuddling and breast-feeding and being carried in close contact is a simulative substitute for intra-uterine oneness). I seem to recall that the Surrealist Salvador Dali used to sleep in water to re-create the intra-uterine oneness. That oneness is divine or (if you accept the physical as a ‘giant’ extended metaphor for the spiritual) is representative of at-one-ness with God (or the Whole) – we individuate and then our life’s quest is to re-integrate!
The loss of the perfect divine state is sometimes described as the Fall – we fell from oneness to separation. It is being separate and yearning for one-ness that is the important thing. Some would say that the over-use and mis-use of ‘sin’ is an invention and distortion utilized by religious men to control others – instead of nurturing others towards a re-establishment of oneness, personally and socially. The life quest includes a) having temporary experiences of oneness and b) managing the separation in the light of the implications of the oneness, c) distinguishing between the fool’s gold of drugs and alcohol and the true ‘wine of astonishment’.
Deep in the fabric of our selves intra-uterine experience as well as childhood experience is embedded, and the unresolved is continuously re-experienced is in some way, shape or form – dreams and patterns of behaviour being two ways. In the Womb is registered the first sensations to do with a sense of place, of safety, or nurturance – and presumably time. Included must be a sense of presence and of pulse, and rhythm, and heart-beat – the very foundations of being.
Toward the building of an extended-metaphor – (poetry c.f. to discursive argument)
The Big Top/Grand Chapiteau like the womb is a place of shelter and warmth and togetherness. The entrance to the ring is a matrix, an interface, between what goes on in the magic circle and the backstage and beyond the wider world. The circus ring as well as offering echoes of the womb also echoes eternity, timelessness – as does the wedding ring. The circus acts are the movements of our dreams, our deepest needs of unresolved tensions. Finally we are disgorged into the night and back into our bourgeois-structured life. Circus like all art forms entertains to heal. Circus like all art forms invites us to re-connect more fully with life’s vitality. Two great artists who understood this are Charles Dickens in Hard Times and Wim Wenders in his film Wings of Desire. These two great works and others are discussed by Dr Helen Stoddart in ‘Rings of Desire’ .
The degeneration of our age is an imbalance – we create people who need an excess of stimulation because they have an insufficiency of sensibility. The violent control of the imagination by the instrumentality of a computer game becomes a norm that prevents deep joyous pleasure in the simple – including simple clowning. Yet fragments of the awe and wonder from childhood stir. Violence is a reaction to the frustration of not realizing the soul’s deeper yearnings. Abuse of self, or others, comes about when the soul’s deeper yearnings can neither be articulated nor satisfied.
Part VI – Conclusion – An aesthetic of longing & hope
“Lord, I am a prisoner of hope.” (a favourite saying of Archbishop Tutu)
Conclusion
I have travelled quite a way from my original excitement about the (New) circus which started with the idea that the circus provided two things a) an extended metaphor for true (holistic) education and b) a means for the theory and practice of the physical, when using a holistic model of education – a means which as Bolton says does not have the disadvantages of competitive sport. I have suggested that Maslow’s hierarchy of needs provides us with the structure for an aesthetic of the circus – and have sketched some of the dynamics in and around the ‘transcendent need level’. Now, tentatively, I have suggested a way of looking at circus as the re-presentation of the arena in which our inner life plays, and re-plays, the dynamic flows of spirit that well up from the deeper places of being human.
Circus is enjoyment in seeing the ordered world dis-ordered – as in the antics of the white-faced clowns. It is enjoyment and wonder at seeing the impossible happen – as in those who fly. Circus is also at the most challenging level the enactment of magical happiness, of our fears and of our deepest yearnings. Those yearnings include our yearning to be at one with ourselves and with that which is not our self – that Whole of which we are all part, and which some call God.
BIBLIOGRAPHY (to be completed)
Brockelman Thomas P. (2001) The Frame and the Mirror: On Collage and Postmodernism, Northwestern Uni Press
Carey John (2005) What Good Are the Arts, London: Faber and Faber
Fairchild Andrea Weltzl (1991) Describing Aesthetic Experience: Creating a Model in CANADIAN JOURNAL OF
EDUCATION 16:3 (1991)
Hick, John, (1981) Mystical Experience as Cognition in Understanding Mysticism, ed. Richard Woods, London: The
Athlone Press
Wilson Ame ‘Perspectives’: Ohio University Autumn/Winter 2002
http://news.research.ohiou.edu/perspectives/archives/0301/anth_2.htm
Shlain Leonard (1998) The Alphabet versus the Goddess: the conflict between Word and Image, London: Viking Children’s Books
ENDNOTES
[1][1] The following notes on Mysticism from Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 1999, 38(1): 175-482 175 might be useful.
Mystics and mysticism have long played important roles in major religions of the East and West, and mysticism is a central topic of concern to those interested in understanding religious experience. Much of the current empirical research has been facilitated by the theoretical formulations of mysticism by philosopher Stace (1960). Stace (1960: 78-79, 110-11, 131-32) distinguished two related types of mysticism, which he called “introvertive” and “extrovertive.” Both types share five criteria.
The mystical experience of both types is
1 Noetic – It is not perceived as mere “subjective” experience or an “emotional” experience; rather, it is a valid source of knowledge.
2 Ineffable – It cannot be described in words.
3 Holy – It is “religious” but not necessarily related to a particular theology.
4 Characterized by positive affect – It is a profound yet pleasurable experience
5 Paradoxical – It defies logic.
Extroversive mystical experience is also
a) Characterized by an inner subjectivity to all things. In some sense, all things are “alive”.
b) Characterized by a perception of unity in the diversity of things.
Introversive mystical experience is also
a) Perceived as timeless and spaceless.
b) One of a “void,” that is, a consciousness devoid of any content or a dissolution of the sense of self.
Whether the experience is extrovertive or introvertive, it is generally agreed by scholars that a sense of unity fundamentally characterizes mysticism. The former is an experience of unity in diversity; the latter is an experience of unity without content in what has been called a “pure consciousness event” (Forman 1990: 8; cf. Stace 1960: 85-86)
Stace’s criteria make it clear that the mysticism under discussion is distinct from what might be labeled paranormal or psychic experiences ……. These phenomena are not included in the conceptual framework of Stace and are also considered, at best, accidental characteristics by influential religious mystics.
Many scholars have also distinguished mysticism proper, as described by Stace, from a numinous experience in which a believer is responding to a perceived “holy other,” sometimes variously named, for example, God, Allah, or Yahweh. Otto’s Idea of the Holy (1917/1958) is considered the classic interpretation of this type of mysticism. The numinous experience tends to have a personal quality to it, in that the believer feels he or she is in communion with the divine being. Mysticism proper tends to emphasize impersonal experiences such as unity, timelessness, spacelessness, and void.
[1][2] SEE for example http://www.websophia.com/faces/beckett.html
[i][i] For a discussion of kitsch see http://www.worldofkitsch.com/about/definition.html For example: kitsch kich noun. trash; art, literature, fashion, etc dismissed as being of merely popular taste or appeal, vulgar, sentimental or sometimes pretentious. Also adjective. kitsch’ily adverb. kitsch’y adjective. [German] Definition from Larousse plc.
[ii][ii] Amazon sell the DVD version for less than 36.00!
[iii][iii] A search for definitions provided nine and since all add something I have included them here. For example Jung’s definition includes the idea of being autonomous. The cognitive science definition includes the idea of identification, or mystical experience, as being ‘absorbed’ into something.
-
the division of the world into separate persons or things.
www.willdurant.com/glossary.htm
-
(in·di·vid·u·a·tion) (in²d[ibreve]-vid²ua¢sh[schwa]n) 1. the process of developing individual characteristics. 2. differential regional activity in the embryo occurring in response to organizer influence.
www.merckmedicus.com/pp/us/hcp/thcp_dorlands_content.jsp
-
A process of differentiation, the end result of which is development of the individual personality that is separate and distinct from all others.
suicideandmentalhealthassociationinternational.org/mhglossary2.html
-
The process of forming and specializing one’s individual nature. It is the developmental process of the psychological individual or personality
www.schuelers.com/ChaosPsyche/glossary.htm
-
The conscious realization of one’s unique psychological reality, including both strengths and limitations. It leads to the experience of the Self as the regulating center of the psyche. Individuation is a process informed by the archetypal idea of wholeness which in turn depends on a vital relationship between ego and unconscious. The aim is not to overcome one’s personal psychology, to become perfect, but to become familiar with it. Thus individuation involves an increasing awareness of one’s unique psychological reality, including personal strengths and limitations, and at the same time a deeper appreciation of humanity in general.
www.selfcompass.com/jung/glossary.html
-
“Individuation means becoming an ‘in-dividual,’ and, insofar as ‘individuality’ embraces our innermost, last, and incomparable uniqueness, it also implies becoming one’s own self.” — CG Jung, Two Essays on Analytical Psychology, par. 266.
www.bemyastrologer.com/definitionsofjungianterms.html
-
individualization: discriminating the individual from the generic group or species
-
individuality: the quality of being individual; “so absorbed by the movement that she lost all sense of individuality”
www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.1
-
Individuation comprises the processes whereby the undifferentiated becomes or develops individual characteristics, or the opposite process, by which components of an individual are integrated into a more indivisible whole. The term serves sociologists, psychologists, philosophers, theologians and embryologists, among others, and thus has been variously defined by different scholars, including Sigmund Freud, Carl Jung, and Charles Darwin.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Individuation
[iii][iv] I subsequently found out that Prof Wilson had died very prematurely a short while ago. Her Masters became the only doctoral thesis on Circle du Soleil.
[v][v] God moves in a mysterious way
His wonders to perform;
He plants his footsteps in the sea
And rides upon the storm.
– William Cowper, Christian Hymn–Light Shining out of Darkness
If there is an inbuilt antipathy to circus, as with gypsies and travelers, is the source a more fundamentalist like belief that to perform ‘wondrous’ acts is sacrilegious?
—–0—–
All postings to this site relate to the central model in the PhD. Summaries are HERE



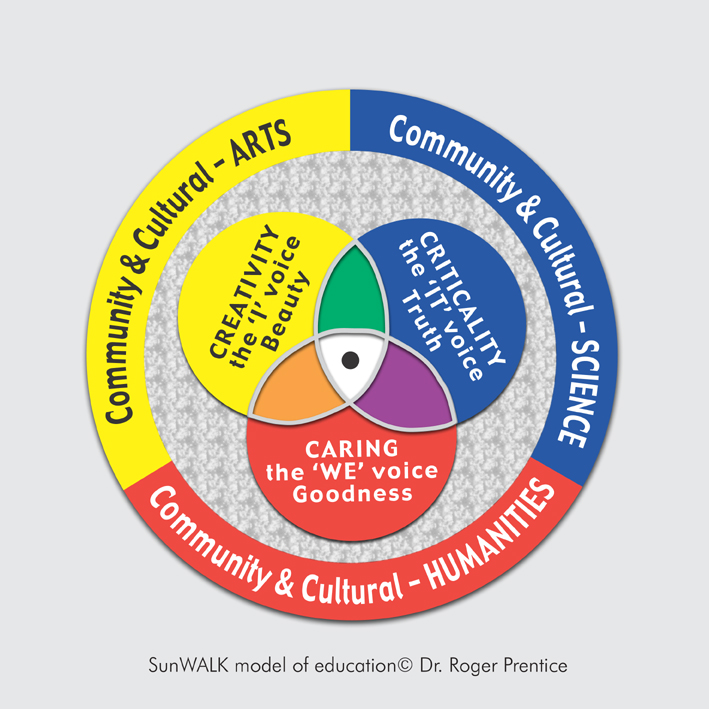

 Photo by: Andre Kertesz – source
Photo by: Andre Kertesz – source






 Source Wiki on Meditation
Source Wiki on Meditation Source
Source


 Source
Source